Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 5:Trisomy 21"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Images == <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> File:IPLab5Downs1.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of cells obtained by amniocentesis that were stained using FISH. The cell...") |
Seung Park (talk | contribs) (→Images) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| + | This 44-year-old woman was 12 weeks pregnant with her third child when routine blood work showed a maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein level that was lower than expected for her stage of pregnancy. At 15-weeks of gestation she underwent ultrasound-guided amniocentesis and samples of the fluid containing cells were smeared onto glass slides for fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). The remainder of the sample was spun down and the fluid was sent for analysis and the cells were cultured for karyotyping. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Findings == | ||
| + | FISH demonstrated three copies of chromosome 21. The patient was informed of these results and was told that definitive results from the karyotyping studies would take several days. The patient was referred to a medical geneticist for counseling. | ||
| + | |||
== Images == | == Images == | ||
<gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 14: | ||
File:IPLab5Downs6.jpg|This is a karyotype of a patient with Turner syndrome (45, X). | File:IPLab5Downs6.jpg|This is a karyotype of a patient with Turner syndrome (45, X). | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="Why are alpha-fetoprotein levels tested in maternal serum? What is the significance of a low alpha-fetoprotein level?">Increased or decreased alpha-fetoprotein levels are indicative of neural tube defects or Down syndrome, respectively. A low alpha-fetoprotein level along with low unconjugated estriol and elevated hCG suggest an increased risk for Down syndrome. Further testing is warranted.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the most common cause of trisomy?">Meiotic nondisjunction.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What are some common physical/clinical abnormalities seen in Down syndrome?">Epicanthic folds and flat facial profile, low set ears, simian crease, congenital heart defects, intestinal stenosis, umbilical hernia, hypotonia, predisposition to leukemia.</spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/943216-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Down Syndrome] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/945649-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Klinefelter Syndrome] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/949681-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Turner Syndrome] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/chromosomal_anomalies/overview_of_chromosomal_anomalies.html Merck Manual: Chromosomal Abnormalities] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Garcia-Heras J, Rao PN. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10334476 A brief review of cryptic duplications of 21q as an emerging cause of Down syndrome: practical considerations for accurate detection]. ''Clin Genet'' 1999 Mar;55(3):207-11. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/788-downs_syndrome PEIR Digital Library: Down Syndrome Images] | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/category/143 PEIR Digital Library: Genetics Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/PEDHTML/PEDIDX.html WebPath: Pediatric-Perinatal Pathology] | ||
{{IPLab 5}} | {{IPLab 5}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 5]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 5]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:33, 30 August 2013
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 44-year-old woman was 12 weeks pregnant with her third child when routine blood work showed a maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein level that was lower than expected for her stage of pregnancy. At 15-weeks of gestation she underwent ultrasound-guided amniocentesis and samples of the fluid containing cells were smeared onto glass slides for fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). The remainder of the sample was spun down and the fluid was sent for analysis and the cells were cultured for karyotyping.
Findings[edit]
FISH demonstrated three copies of chromosome 21. The patient was informed of these results and was told that definitive results from the karyotyping studies would take several days. The patient was referred to a medical geneticist for counseling.
Images[edit]
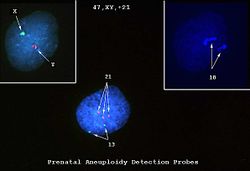
This is a photomicrograph of cells obtained by amniocentesis that were stained using FISH. The cell in panel 1 was stained with markers specific for the X and Y-chromosomes. The cell in panel 2 was stained with a marker specific for chromosome 18. The cell in the center was stained with markers for chromosomes 13 and 21. Note that there are three copies of chromosome 21.
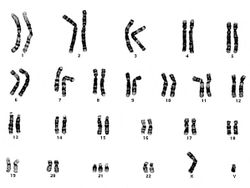
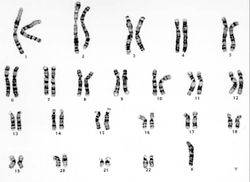
These cells, obtained by amniocentesis, were cultured and then arrested in metaphase. Nuclei from these cells were isolated and stained to demonstrate the banding pattern of each chromosome. This photograph shows a "chromosome spread." Each chromosome is identified and lined up to give a karyotype (next page).
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Down Syndrome
- eMedicine Medical Library: Klinefelter Syndrome
- eMedicine Medical Library: Turner Syndrome
- Merck Manual: Chromosomal Abnormalities
Journal Articles[edit]
- Garcia-Heras J, Rao PN. A brief review of cryptic duplications of 21q as an emerging cause of Down syndrome: practical considerations for accurate detection. Clin Genet 1999 Mar;55(3):207-11.
Images[edit]
- PEIR Digital Library: Down Syndrome Images
- PEIR Digital Library: Genetics Images
- WebPath: Pediatric-Perinatal Pathology
| |||||
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a serum glycoprotein produced during pregnancy by the yolk sac, fetal GI tract, and fetal liver. Elevated serum AFP levels in a pregnant woman can be an indication of a fetal neural tube defect (or something as common as multiple pregnancy). Open fetal neural tube defects allow alpha-fetoprotein to leak into the amniotic fluid, from which it crosses the placenta and enters the maternal bloodstream. Elevated maternal AFP is an indication for amniocentesis (of which an AFP level of amniotic fluid is routine) and an ultrasound. The combination of these two tests are very reliable in detecting neural tube defects.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a serum glycoprotein produced during pregnancy by the yolk sac, fetal GI tract, and fetal liver. Elevated serum AFP levels in a pregnant woman can be an indication of a fetal neural tube defect (or something as common as multiple pregnancy). Decreased serum levels are indicative of trisomy 21.
Amniocentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted transabdominally through the uterus, into the amniotic sac, and amniotic fluid is withdrawn.
FISH uses a fluorescent-labeled antibody specific for a particular chromosome.