Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 6:Glomerulonephritis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == Clinical Summary == | + | == Clinical Summary == |
| − | + | This 17-year-old white male had end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis for 10 years. For the previous four years he had hypertension which slowly increased to about 180/120 mm Hg. Laboratory findings included a greatly elevated BUN and creatinine. He was admitted for bilateral nephrectomy and discharged in satisfactory condition on the 10th postoperative day. He was to be contacted in the future for transplantation. | |
| − | == Autopsy Findings == | + | == Autopsy Findings == |
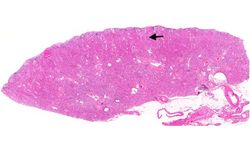
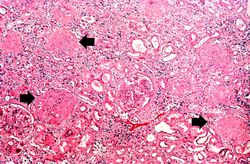
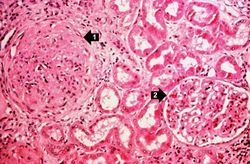
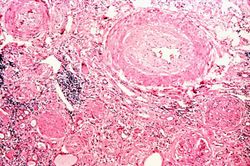
| − | The | + | The left (97 grams) and right (88 grams) kidneys were of similar appearance. Cortices were pale, diffusely granular with a few 1-2 mm cysts. On being sectioned, the cortex of each kidney was thin (4-5 mm) and pale. Renal medullae were pale yellow-tan in color and there was abundant peripelvic fat. The ureters, pelvis, calyces and hilar vessels showed no abnormalities. |
== Images == | == Images == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
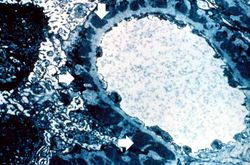
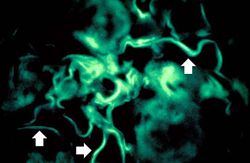
File:IPLab6GN10.jpg|For comparison this is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome. The linear (arrows) immunofluorescence is characteristic of Goodpasture's syndrome. | File:IPLab6GN10.jpg|For comparison this is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome. The linear (arrows) immunofluorescence is characteristic of Goodpasture's syndrome. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab6GN</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the usual clinical course of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis?">One to two weeks after infection (usually sore throat or skin infection) by certain types of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, patients develop malaise, fever, nausea, oliguria, and hematuria. Most patients recover with conservative treatment aimed at maintaining sodium and water balance. The renal injury usually resolves with no loss of function.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the pathogenetic mechanism of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis?">Patients have elevated antibody titers to streptococcal antigens, decreased complement levels, and accumulations of immune complexes and complement in the glomeruli suggesting immune complex mediated glomerular injury. Some streptococcal antigens (endostreptosin and several cationic antigens) have been demonstrated on the glomerular basement membrane. Thus, it is not known for sure if the glomerular damage is caused by circulating antigen antibody complexes, antibodies attacking streptococcal antigens that are attached to the basement membrane, or a combination of both processes. In any event, antibodies bind to antigens, activate complement, and cause damage to the glomeruli. | ||
| + | </spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/429314-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Assessment and Management of the Renal Transplant Patient] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/240337-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/glomerular_disorders/nephritic_syndrome.html Merck Manual: Nephritic Syndrome] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/chronic_kidney_disease/chronic_kidney_disease.html Merck Manual: Chronic Kidney Disease] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/renal_replacement_therapy/hemodialysis.html Merck Manual: Hemodialysis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/immunology_allergic_disorders/transplantation/kidney_transplantation.html Merck Manual: Kidney Transplantation] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Lan HY, Yang N, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Yu XQ, Mu W, Isbel NM, Metz CN, Bucala R, Atkins RC. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10652026 Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human glomerulonephritis]. ''Kidney Int'' 2000 Feb;57(2):499-509. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/226-glomerulonephritis PEIR Digital Library: Glomerulonephritis Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/RENAHTML/RENALIDX.html#8 WebPath: Glomerulonephritis] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 1:Kidney Infarction|Lab 1: Kidney: Infarction (Coagulative Necrosis)]] | ||
{{IPLab 6}} | {{IPLab 6}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:19, 3 January 2014
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 17-year-old white male had end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis for 10 years. For the previous four years he had hypertension which slowly increased to about 180/120 mm Hg. Laboratory findings included a greatly elevated BUN and creatinine. He was admitted for bilateral nephrectomy and discharged in satisfactory condition on the 10th postoperative day. He was to be contacted in the future for transplantation.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
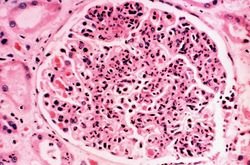
The left (97 grams) and right (88 grams) kidneys were of similar appearance. Cortices were pale, diffusely granular with a few 1-2 mm cysts. On being sectioned, the cortex of each kidney was thin (4-5 mm) and pale. Renal medullae were pale yellow-tan in color and there was abundant peripelvic fat. The ureters, pelvis, calyces and hilar vessels showed no abnormalities.
Images[edit]
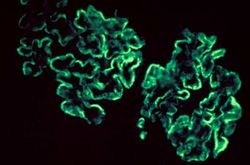
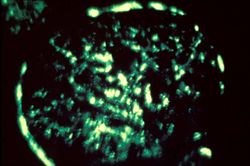
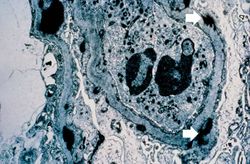
This immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a case of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis shows a granular immunofluorescence pattern consistent with immune complex disease. The primary antibody used for this staining was specific for IgG; however antibodies for complement would show a similar pattern.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Assessment and Management of the Renal Transplant Patient
- eMedicine Medical Library: Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis
- Merck Manual: Nephritic Syndrome
- Merck Manual: Chronic Kidney Disease
- Merck Manual: Hemodialysis
- Merck Manual: Kidney Transplantation
Journal Articles[edit]
- Lan HY, Yang N, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Yu XQ, Mu W, Isbel NM, Metz CN, Bucala R, Atkins RC. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2000 Feb;57(2):499-509.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
A normal alkaline phosphatase is 39 to 117 U/L.
These tests are measures of kidney function. High levels mean low function.
A normal kidney weighs 157 grams (range: 115 to 220 grams).
A normal kidney weighs 157 grams (range: 115 to 220 grams).
Oliguria is the occurrence of decreased urine output.
Hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine.