Revision as of 22:28, 13 November 2013
Clinical History
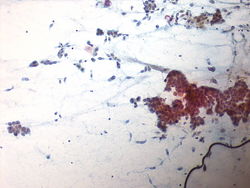
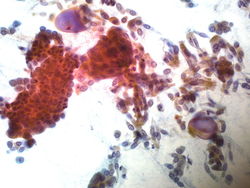
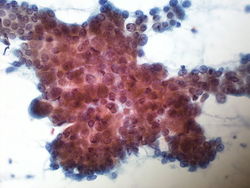
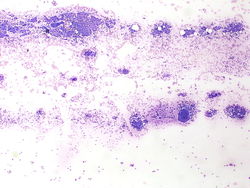
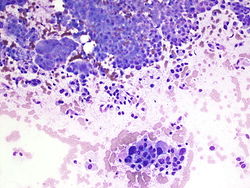
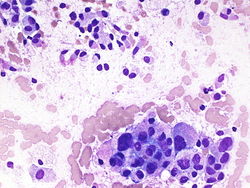
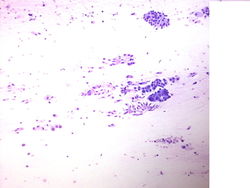
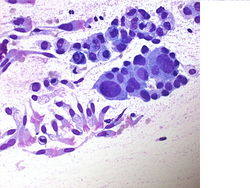
55 year old male with a right upper lobe lung mass and mediastinal adenopathy.
The patient is a smoker.
Cytology
Resident Questions
- EGFR testing is performed on these tumors to select patients for tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)therapy (Gefitinib).
- Patients with EML4-ALK fusion, respond to ALK inhibitor (ALKI) (Crizotinib)
- Deletion and inversion on Chromosome 2p
- Patients with KRAS or BRAF mutation do not respond to TKI, ALKI
- KRAS mutations tend to be an adverse prognostic sign
- Seen in mucinous type tumors, smokers and those of non-Asian ancestry
- Most common mutations are in codons 12 and 13 of exon 2
- EGFR
- Point mutation or substitution mutation in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain
- Sensitive to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Exons 19 deletion
- Exon 21 L858R
- Exon 18 G719
- Resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Exon 20 (insertion V769L, S768I)
- Exon 19 (D761Y)
- Treatment
- EGFR mutations are found in adenocarcinoma and in some adenosquamous carcinomas
- Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), which stimulates angiogenesis in cancer
- Association between fatal hemoptysis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung treated with Bevacizumab
- Therefore, Bevacizumab is contraindicated for tumors with squamous cell histology
Additional Teaching Points
Immunohistochemistry
- TTF-1 (nuclear stain)
- Thyroid Transcription factor1 regulates transcription of genes specific to the thyroid, lung, and diencephalon
- If metastatic thyroid cancer to the lung is ruled out by morphology or +thyroglobulin; then a +TTF1 supports adenocarcinoma originating from the lung
- P63 (nuclear stain) and 34BE12 (cytoplasmic stain)
- Used for squamous differentiation
- TTF1 is more sensitive than p63
- If a tumor stains for both it is more likely to be adenocarcinoma
- Napsin A(cytoplasmic stain)
- Granular staining pattern
- Marker for adenocarcinoma