Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 2:Metaplasia"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Study Questions) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
This 30-year-old black male was born with a meningocele which was repaired in childhood. Despite repair of the meningocele, this patient continued to have a neurogenic bladder. | This 30-year-old black male was born with a meningocele which was repaired in childhood. Despite repair of the meningocele, this patient continued to have a neurogenic bladder. | ||
| − | Six months previous to this admission, the patient passed a single renal calculus but intravenous | + | Six months previous to this admission, the patient passed a single renal calculus but intravenous pyelogram (IVP) showed left nephrolithiasis (a 1 cm stone in the lower lobe). For 6 months the patient had to be catheterized each day for 6 hours. However, he continued to complain of hesitancy and urgency and suffered occasional urinary tract infections. |
On this admission, a culture of the patient's urine specimen grew Gram-negative bacilli (Proteus species). Cystoscopy showed heavy trabeculation of the bladder with early diverticula and the left ureteral orifice showed squamous metaplasia. The lower pole of the left kidney was removed surgically, following which the patient recovered and was discharged on antibiotics. | On this admission, a culture of the patient's urine specimen grew Gram-negative bacilli (Proteus species). Cystoscopy showed heavy trabeculation of the bladder with early diverticula and the left ureteral orifice showed squamous metaplasia. The lower pole of the left kidney was removed surgically, following which the patient recovered and was discharged on antibiotics. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
File:IPLab2Metaplasia7.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of the trachea from a smoker. Note that the columnar ciliated epithelium has been replaced by squamous epithelium. | File:IPLab2Metaplasia7.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of the trachea from a smoker. Note that the columnar ciliated epithelium has been replaced by squamous epithelium. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | === Kidney: Metaplasia === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab2Metaplasia</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Normal Kidney === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>UAB-Histology-00114</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is a neurogenic bladder and what complications may result from this condition?">A neurogenic bladder is any condition or dysfunction of the urinary bladder caused by a lesion of the central or peripheral nervous system. Complications primarily include stasis, infection, and stone formation.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What factors in this case predisposed to nephrolithiasis?">Stasis and infection.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="Does this metaplastic process predispose to neoplasia?">No.</spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/437096-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Nephrolithiasis] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/453539-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Neurogenic Bladder] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/urinary_calculi/urinary_calculi.html Merck Manual: Urinary Calculi] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/voiding_disorders/neurogenic_bladder.html Merck Manual: Neurogenic Bladder] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/genitourinary_disorders/approach_to_the_genitourinary_patient/evaluation_of_the_renal_patient.html Merck Manual: Approach to the Genitourinary Patient] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1055320709000180 Cellular Mechanisms of Barrett's Esophagus Development]. ''Surg Oncol Clin N Am '' 2009 18:393–410. | ||
| + | * Spechler SJ and Souza RF. [http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1314704 Barrett’s Esophagus]. ''N Engl J Med'' 2014 371:836-45. | ||
| + | * Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. [http://www.biochemsoctrans.org/content/38/2/370 Cellular origin of Barrett’s metaplasia and oesophageal stem cells]. ''Biochem. Soc. Trans'' 2010 38:370–373. | ||
| + | * Mills JC and Sansom OJ. [http://stke.sciencemag.org/content/8/385/re8.full Reserve stem cells: Differentiated cells reprogram to fuel repair, metaplasia, and neoplasia in the adult gastrointestinal tract]. ''Sci. Signal'' 2015 8(385):re8. | ||
| + | * Clouston B and Lawrentschuk N. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bju.12378/full Metaplastic conditions of the bladder]. ''BJU Int''2013 112(Suppl 2):27-31. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/148-bladder/11-urinary PEIR Digital Library: Bladder Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/RENAHTML/RENALIDX.html WebPath: Renal Pathology Images] | ||
{{IPLab 2}} | {{IPLab 2}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 2]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 2]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:37, 8 November 2015
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 30-year-old black male was born with a meningocele which was repaired in childhood. Despite repair of the meningocele, this patient continued to have a neurogenic bladder.
Six months previous to this admission, the patient passed a single renal calculus but intravenous pyelogram (IVP) showed left nephrolithiasis (a 1 cm stone in the lower lobe). For 6 months the patient had to be catheterized each day for 6 hours. However, he continued to complain of hesitancy and urgency and suffered occasional urinary tract infections.
On this admission, a culture of the patient's urine specimen grew Gram-negative bacilli (Proteus species). Cystoscopy showed heavy trabeculation of the bladder with early diverticula and the left ureteral orifice showed squamous metaplasia. The lower pole of the left kidney was removed surgically, following which the patient recovered and was discharged on antibiotics.
Images[edit]
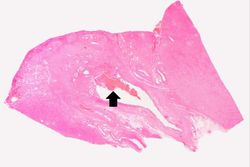
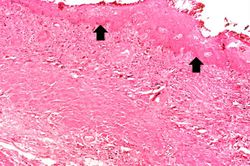
This is a low-power photomicrograph showing the full cortical and medullary thickness of the kidney. Note that there is a dilated calyx containing some red blood cells in the center of the section (arrow). The cortex is markedly thin and has severe lesions of degeneration and atrophy, although these are hard to appreciate at this low magnification.
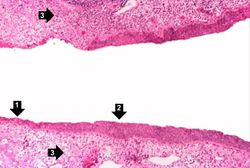
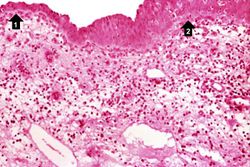
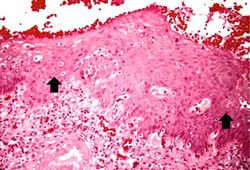
This high-power photomicrograph demonstrates the transitional epithelium lining the renal calyx (1) and the junction (transition zone) to a thicker hyperplastic epithelium (2). Note the inflammatory cells and increased vascular response in the stromal tissue (3) lying beneath the normal transitional epithelium.
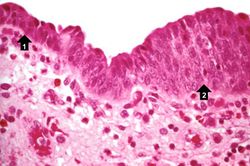
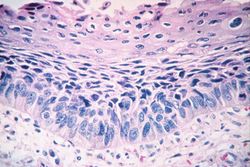
In areas adjacent to the normal transitional epithelium, there are areas of epithelium (arrows) where the epithelial cells have the character of normal squamous epithelium as found in the dermis. However, squamous epithelium is not normal in the renal pelvis. This adaptive change is referred to as squamous metaplasia.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Kidney: Metaplasia[edit]
Normal Kidney[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Nephrolithiasis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Neurogenic Bladder
- Merck Manual: Urinary Calculi
- Merck Manual: Neurogenic Bladder
- Merck Manual: Approach to the Genitourinary Patient
Journal Articles[edit]
- Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. Cellular Mechanisms of Barrett's Esophagus Development. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 2009 18:393–410.
- Spechler SJ and Souza RF. Barrett’s Esophagus. N Engl J Med 2014 371:836-45.
- Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. Cellular origin of Barrett’s metaplasia and oesophageal stem cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2010 38:370–373.
- Mills JC and Sansom OJ. Reserve stem cells: Differentiated cells reprogram to fuel repair, metaplasia, and neoplasia in the adult gastrointestinal tract. Sci. Signal 2015 8(385):re8.
- Clouston B and Lawrentschuk N. Metaplastic conditions of the bladder. BJU Int2013 112(Suppl 2):27-31.
Images[edit]
| |||||
A meningocele is the herniation of the CSF-filled meningeal sac through a vertebral defect.
Neurogenic bladder is a dysfunction of the bladder caused by a nervous system lesion.
A renal calculus is a "kidney stone."
The patient is given an intravenous injection of contrast medium that rapidly enters the urine. Radiographs are then taken to show the passage of the contrast-containing urine through the pelvicaliceal system.
Nephrolithiasis is the presence of a urinary calculus within the kidney.
Hesitancy is the inability to begin the stream of urine.
Urgency is the experience of an intense and immediate desire to void.
Cystoscopy is the direct visual examination of the bladder via a cystoscope.
A bladder diverticulum is an out-pouching of the bladder wall, usually caused by chronic urethral obstruction.