Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 4:Chronic Passive Congestion"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Virtual Microscopy) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
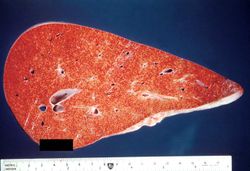
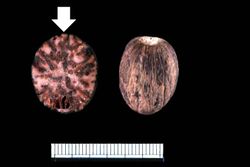
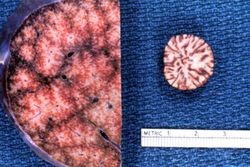
File:IPLab4ChronicPassiveCongestion9.jpg|This is a gross photograph of the cut surface of a liver with chronic passive congestion (left) compared to the cut surface of a nutmeg (right). | File:IPLab4ChronicPassiveCongestion9.jpg|This is a gross photograph of the cut surface of a liver with chronic passive congestion (left) compared to the cut surface of a nutmeg (right). | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | === Liver Chronic Passive Congestion === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab4ChronicPassiveCongestion</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Normal Liver === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>UAB-Histology-00149</peir-vm> | ||
== Study Questions == | == Study Questions == | ||
* <spoiler text="What is the most common cause of chronic passive congestion of the liver?">Right-sided heart failure. Also, obstruction of the inferior vena cava or hepatic vein (usually associated with neoplasia and/or a hypercoagulable state leading to thrombosis) can cause hepatic congestion</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="What is the most common cause of chronic passive congestion of the liver?">Right-sided heart failure. Also, obstruction of the inferior vena cava or hepatic vein (usually associated with neoplasia and/or a hypercoagulable state leading to thrombosis) can cause hepatic congestion</spoiler> | ||
* <spoiler text="Why is the central vein region most severely affected by chronic passive congestion?">The central vein region is farthest away from the arterial (oxygenated) blood so this region has the lowest oxygen tension anyway. With congestion and stasis, this central vein region becomes hypoxic which results in liver cell atrophy and necrosis. The peripheral regions are hypoxic but and develop fatty change. Thus, the dark red, congested, and necrotic central vein region that is surrounded by yellow fatty change gives the morphology that is termed "nutmeg liver."</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="Why is the central vein region most severely affected by chronic passive congestion?">The central vein region is farthest away from the arterial (oxygenated) blood so this region has the lowest oxygen tension anyway. With congestion and stasis, this central vein region becomes hypoxic which results in liver cell atrophy and necrosis. The peripheral regions are hypoxic but and develop fatty change. Thus, the dark red, congested, and necrotic central vein region that is surrounded by yellow fatty change gives the morphology that is termed "nutmeg liver."</spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/151792-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Cardiac Cirrhosis and Congestive Hepatopathy] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/156330-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Myocarditis] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2069746-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Pediatric Congestive Heart Failure] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/hepatic_and_biliary_disorders/fibrosis_and_cirrhosis/cirrhosis.html Merck Manual: Cirrhosis] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Naschitz JE, Slobodin G, Lewis RJ, Zuckerman E, Yeshurun D. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10874271 Heart diseases affecting the liver and liver diseases affecting the heart]. ''Am Heart J'' 2000 Jul;140(1):111-20. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/672-chronic_passive_congestion PEIR Digital Library: Chronic Passive Congestion Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/LIVEHTML/LIVERIDX.html#1 Webpath: Hepatic Pathology] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 8:Hepatitis B|Lab 8: Liver: Hepatitis B]] | ||
{{IPLab 4}} | {{IPLab 4}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 4]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 4]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:17, 16 September 2015
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 57-year-old male was hospitalized with a three-month history of a dry, hacking cough, dyspnea, and chest pain. He was diagnosed as having congestive heart failure due to viral myocarditis. There was no evidence of myocardial infarction, but renal and hepatic functions were decreased. The patient developed refractory congestive heart failure and renal failure. The patient's cardiac index was marginal and he was classified as a having congestive cardiomyopathy. The patient had a cardiorespiratory arrest and died two months after admission.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
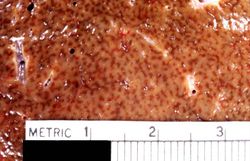
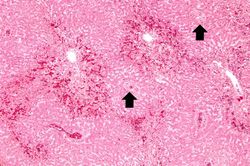
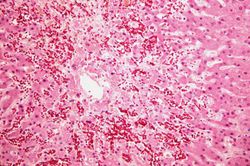
At autopsy the lungs were congested and edematous with evidence of lobar pneumonia. The heart weighed 540 grams and showed 75 to 95% atherosclerotic stenosis of all the major coronary arteries. The right and left ventricles were markedly dilated. The ventricular walls were extremely thin with patchy areas of subendocardial fibrosis. The liver weighed 1630 grams and displayed the classic "nutmeg appearance" of chronic passive hepatic congestion on cut surface.
Images[edit]
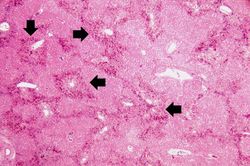
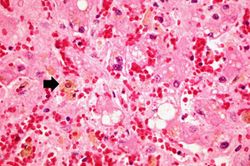
This is a high-power photomicrograph of liver with several macrophages that are distended with a brown pigment (arrow). These resident macrophages (Kupffer cells) are part of the reticuloendothelial system and normally line the sinusoidal spaces in the liver where they phagocytose the RBCs that pool, and eventually die, in the central vein region.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Liver Chronic Passive Congestion[edit]
Normal Liver[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Cardiac Cirrhosis and Congestive Hepatopathy
- eMedicine Medical Library: Myocarditis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Pediatric Congestive Heart Failure
- Merck Manual: Cirrhosis
Journal Articles[edit]
- Naschitz JE, Slobodin G, Lewis RJ, Zuckerman E, Yeshurun D. Heart diseases affecting the liver and liver diseases affecting the heart. Am Heart J 2000 Jul;140(1):111-20.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
| |||||
Viral myocarditis is an inflammatory viral infection of the myocardium.
Myocardial infarction is necrosis of myocardial tissue which occurs as a result of a deprivation of blood supply, and thus oxygen, to the heart tissue. Blockage of blood supply to the myocardium is caused by occlusion of a coronary artery.
Renal failure is the severe reduction of renal function and often leads to reduced urinary output.
Cardiac index is a measure of a patient's cardiac output in relation to body size.
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.
A normal heart weighs 300 grams (range: 270 to 360 grams).
A normal liver weighs 1650 grams (range: 1500 to 1800 grams).
Chronic passive hepatic congestion is a disorder seen in conjunction with right-sided heart failure. In right-sided heart failure, peripheral venous pressures increase and thus reduce outflow from the liver. The result is a chronically congested liver.