Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 5:Gout"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Study Questions) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Study Questions == | == Study Questions == | ||
| − | * <spoiler text="What are the two types of gout and which is more common?">The main type is primary gout which makes up 90% of all cases. In most cases of primary gout the enzyme defect is unknown. In rare cases the enzyme defect is known, but gout symptomatology is the main clinical finding. | + | * <spoiler text="What are the two types of gout and which is more common?">The main type is primary gout which makes up 90% of all cases. In most cases of primary gout the specific enzyme defect is unknown but there is some enzyme abnormality which leads to hyperuricemia and symptoms of gout. In rare cases the specific enzyme defect is known, but gout symptomatology is the main clinical finding. |
In secondary gout the cause of the hyperuricemia is known (e.g. leukemia, renal failure, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome).</spoiler> | In secondary gout the cause of the hyperuricemia is known (e.g. leukemia, renal failure, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome).</spoiler> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10068714 Gout and hyperuricemia]. ''Am Fam Physician'' 1999 Feb 15;59(4):925-34. | * Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10068714 Gout and hyperuricemia]. ''Am Fam Physician'' 1999 Feb 15;59(4):925-34. | ||
* Pittman JR, Bross MH. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10208700 Diagnosis and management of gout]. ''Am Fam Physician'' 1999 Apr 1;59(7):1799-806, 1810. | * Pittman JR, Bross MH. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10208700 Diagnosis and management of gout]. ''Am Fam Physician'' 1999 Apr 1;59(7):1799-806, 1810. | ||
| + | * Qaseem A, Harris RP, Forciea MA. [http://annals.org/aim/article/2578528/management-acute-recurrent-gout-clinical-practice-guideline-from-american-college Management of Acute and Recurrent Gout]. ''Ann Intern Med'' 2016 Nov 1 10;7326/M16-0570. | ||
=== Images === | === Images === | ||
Latest revision as of 12:29, 5 December 2016
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
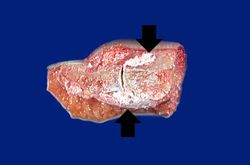
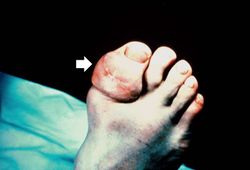
This patient was diagnosed with gout approximately 20 years ago. At that time, he noted the gradual onset of pain in the left knee, followed by swelling, redness and heat, all of which persisted for approximately one month. Shortly thereafter, he had periodic episodes of hot, painful, swollen joints involving the left knee, left ankle, and both first metatarsophalangeal joints. At this time the patient was hospitalized for evaluation of these arthritides. Serum uric acid values on three separate occasions were 8.0, 9.3, and 8.7 mg/dl. In addition to the presence of the painful swollen joints, a gouty tophus was present on the left arm. The patient was readmitted to the hospital from time to time because of acute exacerbations of gouty arthritis. On the most recent hospital admission, a 3-cm tophus was found over the right elbow, as well as several smaller tophi over the right hand.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
The specimen consisted of an elliptically shaped, mottled, yellow-white irregular hard mass, measuring 8.0 x 5.0 x 2.0 cm. in diameter.
Images[edit]
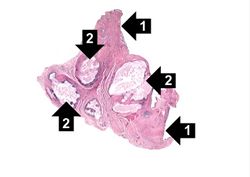
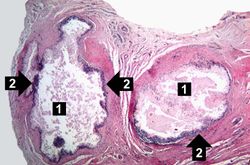
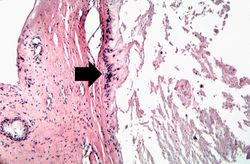
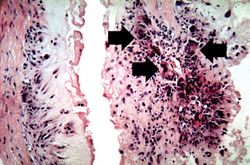
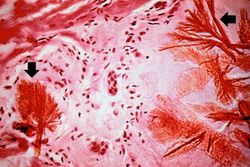
This is a photomicrograph of a tophus that was fixed in alcohol prior to histologic processing. The alcohol fixation preserves the water soluble urate crystals within the tissue. Note the urate crystals visible in this photomicrograph (arrows). Also note the chronic inflammatory reaction in the background.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Gout and Pseudogout
- American Academy of Family Physicians: Gout and Hyperuricemia
Journal Articles[edit]
- Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. Gout and hyperuricemia. Am Fam Physician 1999 Feb 15;59(4):925-34.
- Pittman JR, Bross MH. Diagnosis and management of gout. Am Fam Physician 1999 Apr 1;59(7):1799-806, 1810.
- Qaseem A, Harris RP, Forciea MA. Management of Acute and Recurrent Gout. Ann Intern Med 2016 Nov 1 10;7326/M16-0570.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
| |||||
The normal serum uric acid level for a male is 3.9 to 8.1 mg/dl.
A tophus is a chalky accumulation of urate crystals found in the tissue surrounding a joint.
The normal fibrinogen level is 184 to 412 mg/dL.
Renal failure is the severe reduction of renal function and often leads to reduced urinary output.