Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 7:Malignant Melanoma"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
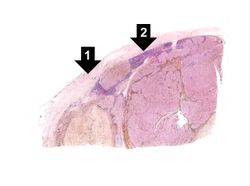
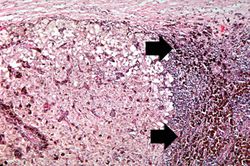
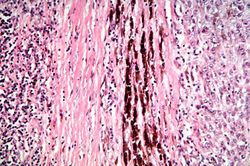
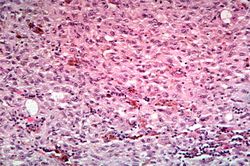
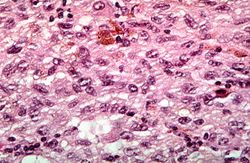
File:IPLab7Melanoma8.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of the main tumor mass showing the cellular details. The individual melanoma cells contain large nuclei with irregular contours having chromatin clumped at the periphery of the nuclear membrane and prominent red (eosinophilic) nucleoli. | File:IPLab7Melanoma8.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of the main tumor mass showing the cellular details. The individual melanoma cells contain large nuclei with irregular contours having chromatin clumped at the periphery of the nuclear membrane and prominent red (eosinophilic) nucleoli. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Question == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What are the possible sites of origin for melanomas?">Most melanomas arise in the skin; however, other sites of origin include the oral and anogenital mucosal surfaces, esophagus, meninges, and the eye.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What are risk factors for developing melanoma?">Sunlight appears to play an important role in the development of skin malignant melanoma. Lightly pigmented individuals are at higher risk for the development of melanoma than darkly pigmented individuals. Sunlight does not seem to be the only predisposing factor, and the presence of a pre-existing nevus (e.g., a dysplastic nevus), hereditary factors, or even exposure to certain carcinogens may play a role in lesion development and evolution.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What role may tumor specific antigens play in development of malignant melanoma?">Approximately 40% of human melanomas express a tumor specific antigen referred to as melanoma antigen-1 (MAGE-1). Molecular analysis has revealed that the gene encoding MAGE-1 is present in normal cells as well as in tumor cells, and there is no evidence that it is mutated in cancer cells. However, as has been seen in some animal tumors, the gene is silent in normal adult cells; whether or not it is expressed during development remains to be determined. CD8+ cytotoxic T cells specific for MAGE-1 can be obtained by culturing tumor cells with patients’ lymphocytes in vitro.</spoiler> | ||
{{IPLab 7}} | {{IPLab 7}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 21 August 2013
Clinical Summary[edit]
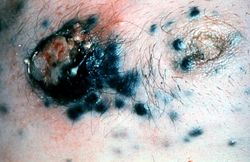
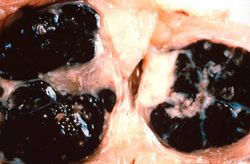
This 68-year-old white male had a local excision of a pigmented lesion (melanoma) on the skin of his back. Three years later he became aware of a "lump" in his left axilla. Examination confirmed the presence of a 2.3-cm nodular lesion. Subsequently, the patient underwent a surgical procedure for removal of axillary lymph nodes.
Images[edit]
Study Question[edit]
Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate--characterized by large discrete prostatic nodules--is a common disorder in men over 50 years of age. The nodules cause the prostate to be enlarged and to have an increased weight. The human prostate is surrounded by a restrictive capsule. These nodules cause increased pressure within the capsule which leads to constriction of the urethra as it passes through the prostate. Urethral constriction leads to retention of urine.