From Pathology Education Instructional Resource
Images
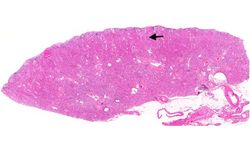
This is a low-power photomicrograph of a saggital section of end stage chronic glomerulonephritis (GN). Note the marked thinning of the cortex (arrow).
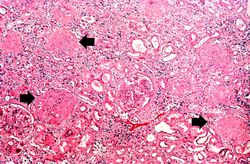
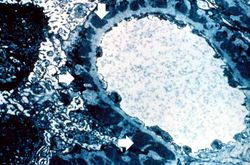
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (arrows) and glomeruli with thick basement membranes.
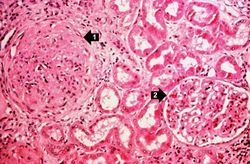
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (1) and glomeruli with thickened basement membranes (2).
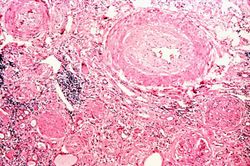
This is a photomicrograph of interstitial and vascular lesions in end stage renal disease.
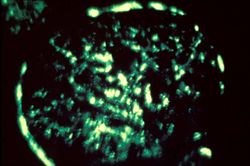
This is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of granular membranous immunofluorescence (immune complex disease). The antibody used for these studies was specific for IgG.
This is an electron micrograph of subepithelial granular electron dense deposits (arrows) which correspond to the granular immunofluorescence seen in the previous image.
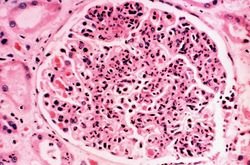
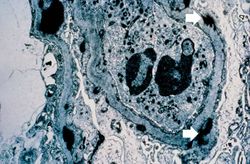
This is a photomicrograph of a glomerulus from another case with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. In this case the immune complex glomerular disease is ongoing with necrosis and accumulation of neutrophils in the glomerulus.
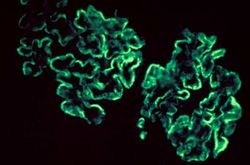
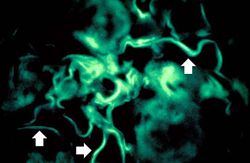
This immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a case of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis shows a granular immunofluorescence pattern consistent with immune complex disease. The primary antibody used for this staining was specific for IgG; however antibodies for complement would show a similar pattern.
This electron micrograph demonstrates scattered subepithelial dense deposits (arrows) and a polymorphonuclear leukocyte in the lumen.
For comparison this is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome. The linear (arrows) immunofluorescence is characteristic of Goodpasture's syndrome.