Clinical Summary
The patient is an 64 year old white male who presented with left sided back pain. Imaging showed a left perinephric retroperitoneal hematoma and a left renal lower pole cystic lesion with hemorrhage. Additional imaging showed numerous pulmonary lesions. A endobronchial ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration was scheduled.
Past Medical History
- Congestive heart failure
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ischemic heart disease
Past Surgical History
- Coronary stent placement
- Implant of AICD
Clinical Plan
The concern is a primary renal malignancy with metastatic disease to lungs. An endobronchial ultrasound guided FNA is scheduled.
Radiology
- CT Abdomen shows a large perinephric hematoma and large low anterior structure in left lower pole suspicious for a hemorrhagic renal cell carcinoma.
- CT Chest shows multiple small lung lesions measuring up to 13x12 mm in greatest dimension.
Pathology
Cytology
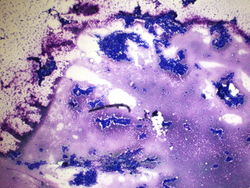
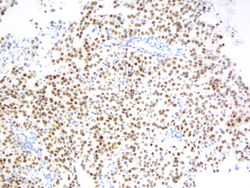
4x magnification of a 4R lymph node. There is a polymorphic lymphoid population with scattered large atypical cells.
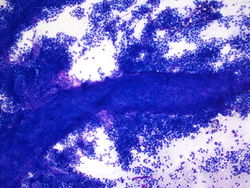
20x magnification of paracaval lymph node. There are small lymphocytes with background lymphoglandular bodies. Scattered eosinophils and large atypical cells with prominent nucleoli.
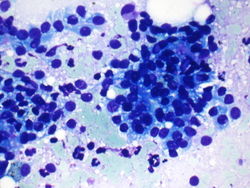
40x magnification of paracaval lymph node. There are atypical binucleated cells among the large atypical cells.
40x magnification of paracaval lymph node. There are atypical binucleated cells among the large atypical cells.
40x magnification of paracaval lymph node. There are atypical binucleated cells among the large atypical cells.
Resident Questions
These groups of cells demonstrate malignant appearing cells in a background of an otherwise benign appearing lymphoid background. The atypical cells are scattered, with large nucleoli and several binucleate forms. In addition, there seem to be an increased number of eosinophils in the background. The differential diagnosis includes Hodgkin lymphoma; however, the possibility of the large atypical cells being melanoma cannot be ruled out.
For this patient, we recommended that the radiologist perform a biopsy of the lesion so that it could be sent for immunohistochemical workup. Since the overall percentage of the atypical cells were low, we were worried that a cell block would not contain enough of the malignant cells for additional stains. We also sent the lymph node for flow since a hematologic malignancy was suspected; however, with Hodgkin lymphoma, we don't expect any diagnostic findings from flow cytometry.
CD15, CD30, and PAX5 would stain tumor cells in Hodkin lymphoma. Mart1, HMB45, and S100 could be used to rule out melanoma. Other additional stain in a lymphoma versus melanoma workup might include CD3, CD20, and keratin.
Click here to toggle the diagnosis and case discussion.
Final Diagnosis
Cytology
- Positive for malignancy, the differential diagnosis includes melanoma and Hodgkin lymphoma.
Biopsy
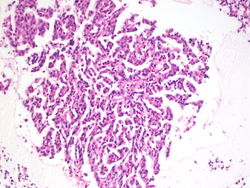
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma, favor mixed type.
Case Discussion
This is a classic case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.