File:IPLab2Hyperplasia9.jpg
Revision as of 15:29, 19 August 2013 by Peter Anderson (talk | contribs) (This kidney was removed from another autopsy patient who had prostatic hyperplasia resulting in marked urinary retention and back-flow of urine from the bladder into the ureters and renal pelvis. The increased pressure inside the renal pelvis resulted ...)
IPLab2Hyperplasia9.jpg (666 × 450 pixels, file size: 37 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
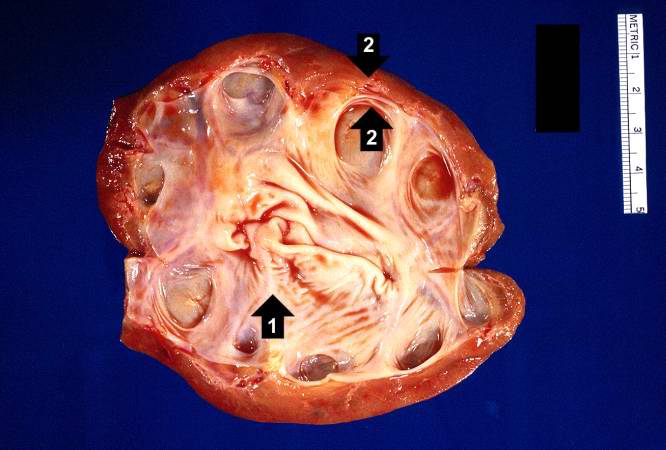
This kidney was removed from another autopsy patient who had prostatic hyperplasia resulting in marked urinary retention and back-flow of urine from the bladder into the ureters and renal pelvis. The increased pressure inside the renal pelvis resulted in dilation of the renal pelvis (1) and pressure atrophy of the cortex (2). This change in the kidney is called hydronephrosis.
"Urinary retention" is the inability to fully empty the bladder during urination.
Hydronephrosis is dilation of the renal pelvis and atrophy of the cortex due to increase pressure from retained urine.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:29, 19 August 2013 |  | 666 × 450 (37 KB) | Peter Anderson (talk | contribs) | This kidney was removed from another autopsy patient who had prostatic hyperplasia resulting in marked urinary retention and back-flow of urine from the bladder into the ureters and renal pelvis. The increased pressure inside the renal pelvis resulted ... |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page links to this file: